Expected odds ratio This is what you expect the odds ratio to be, ie, the odds of the outcome given presence of the property you are looking for an association with relative to the same outcome in the absence of that property This can often be determined by using the results from a previous study, or by running a small pilot studyEnglishwise, they are correct it is the odds and the odds are based on a ratio calculation It is not , however, the odds ratio that is talked about when results are reported The odds ratio when results are reported refers to the ratio of two odds or, if you prefer, the ratio of two odds ratios That is, let us writeLet us now look at the relation between the relative risk and the odds ratio (Zhang and Yu, 1998) OR= ˇ 1 1 1ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 = ˇ ˇ 2 1 2 1 1 = RR 2 1 (21) From this we see that OR is always further away from 1 than RR But, more importantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998)

The Diagnostic Odds Ratio A Single Indicator Of Test Performance Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology
What is the difference between odds ratio and hazard ratio
What is the difference between odds ratio and hazard ratio-And a risk of 095 is equivalent to odds of 19 Measures of effect for clinical trials with dichotomous outcomes involve comparing either risks or odds from two intervention groups To compare them we can look at their ratio (risk ratio or odds ratio) or their difference in risk (riskA value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statistical




Bravură Fii Entuziasmat Analitic Odds Ratio Calculator Callumluckwellfinalyear Com
Risk ratios At a minimum, the only change that needs to be done to get risk ratios is to change the link function that relates the mean value of the response variable to the linear predictor For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean);After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 14 (mortality is 14 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium) Because the incidence rate in the nondelirium group is high, the odds ratio exaggerates the true risk demonstrated inTo the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs) the magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrence (eg, no death;
In prospective trials, it is simply a different way of expressing this association than relative riskTo calculate the odds ratio, we use one of the following formulas (both give the same outcome) Example 2 We compare smokers and nonsmokers with regard to the presence of ischemic heart disease The following table shows the results Example 2 We can now calculate the odds ratio (10/40) / (5/45) = 225More on the Odds Ratio Ranges from 0 to infinity Tends to be skewed (ie not symmetric) "protective" odds ratios range from 0 to 1 "increased risk" odds ratios range from 1 to Example "Women are at 144 times the risk/chance of men" "Men are at 069 times the risk
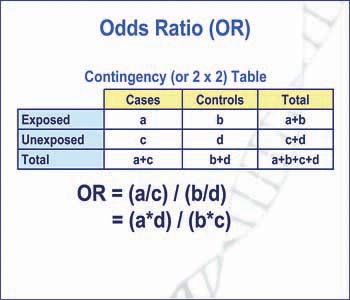
The ratio of two cumulative incidences is called the cumulative incidence risk ratio An odds ratio is the ratio of two odds for example a/b / c/d In epidemiological parlance it is the odds of infection for those exposed to a risk factor, divided by the odds of infection for those not exposed to that risk factorRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the odds ratio Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently (




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
If the outcome is rare in both exposed and unexposed persons, the odds ratio (A/B/C/D) will approximate the risk ratio (A/(A B)/C/(C D)) However, when the study outcome is common and the risk ratio is not close to 1, the odds ratio will be further from 1 compared with the risk ratio9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are theThe more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratio




The Diagnostic Odds Ratio A Single Indicator Of Test Performance Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology



Q Tbn And9gcs7g3 Oy3gxo7fbk7uvklwexnnbqcmd7m5bqd Ghq64ww9hd4dh Usqp Cau
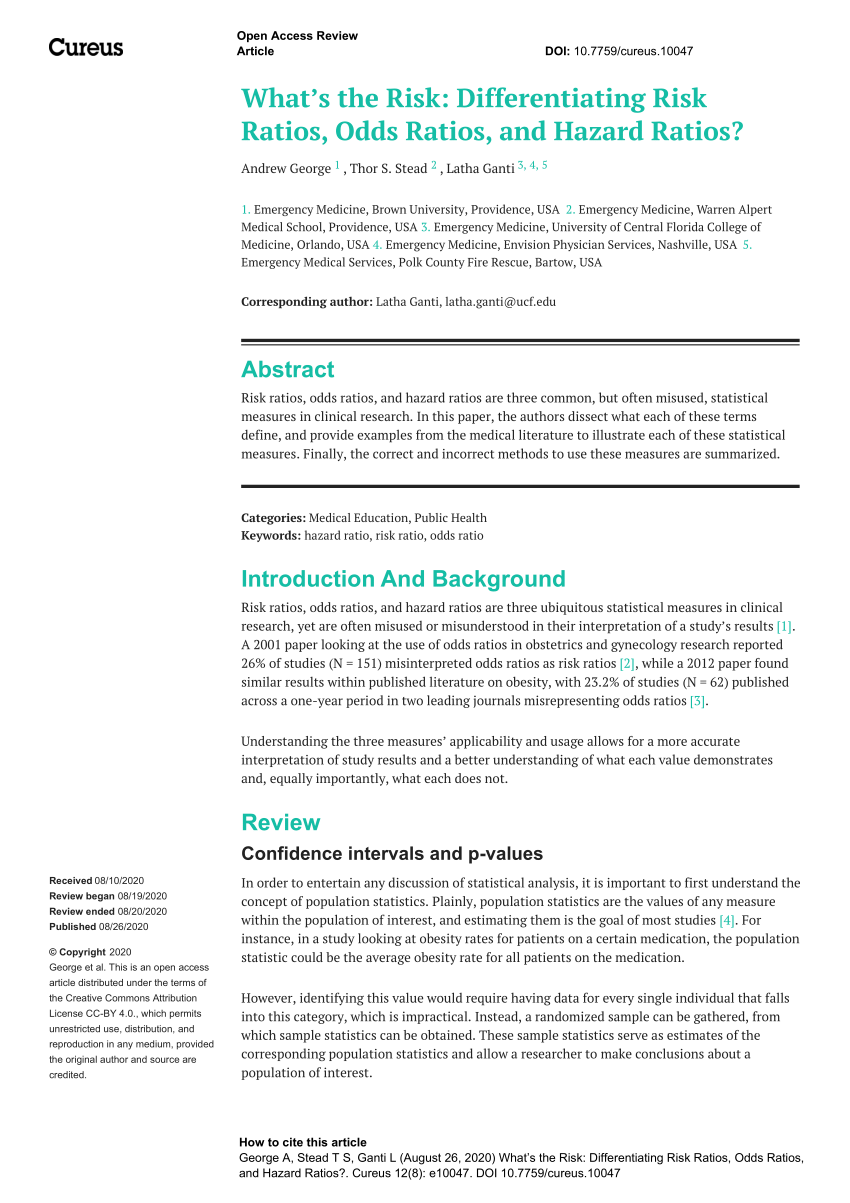
Overview The term measures of effect includes ratios, differences, relative risks (RR), odds ratios Population attributable risk and population attributable risk factor are also measures of effect but more specifically are measures of population impact Ratios and Differences Risks (defined as the probability of a new occurrence disease among individuals in an initially diseaseAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% = 01% x 10), more than 10 times higher Definition The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed) Example I often think food poisoning is a good scenario to consider when interpretting ORs Imagine a group of friends went out to



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream



44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 Review 1 Similar To The Risk Ratio Here Are The Guidelines For Calculating A Confidence Interval For 2 Independent Samples And The Odds Ratio As The Parameter Of Interest 2 Note That Calculation Of The Confidence
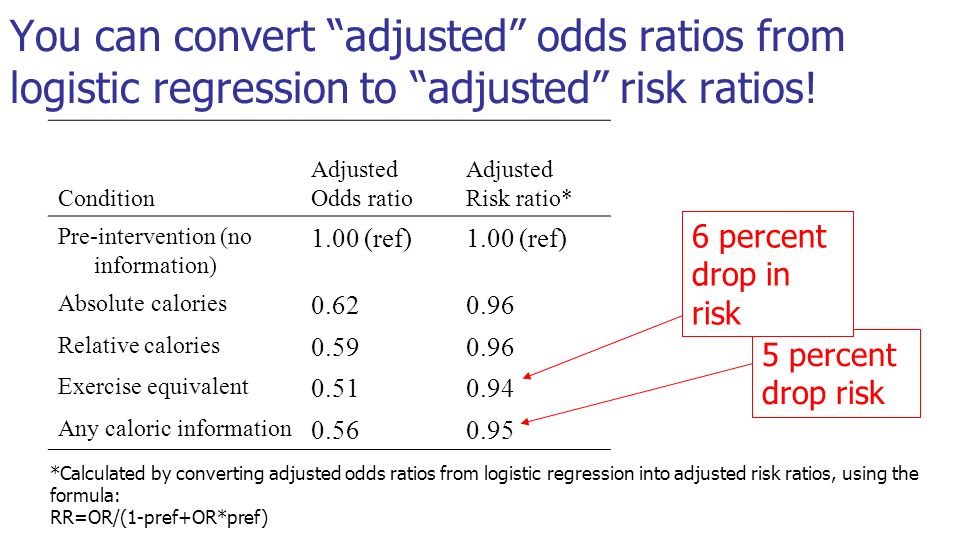
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table The ratio of these two probabilities R1/R2 is the relative risk or risk ratio Pretty intuitive If the program worked, the relative risk should be smaller than one, since the risk of failing should be smaller in the tutored group If the relative risk is 1, the tutoring made no difference at all




Measuring Of Risk



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios
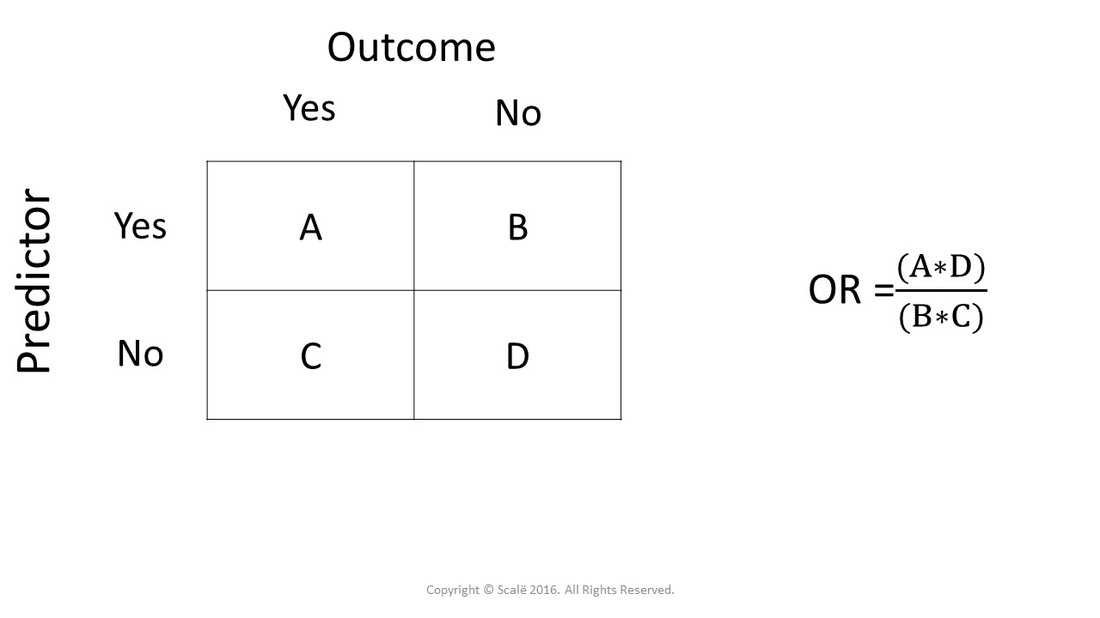
In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;Diagnostic odds ratio In medical testing with binary classification, the diagnostic odds ratio ( DOR) is a measure of the effectiveness of a diagnostic test It is defined as the ratio of the odds of the test being positive if the subject has a disease relative to the odds of the test being positive if the subject does not have the disease Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
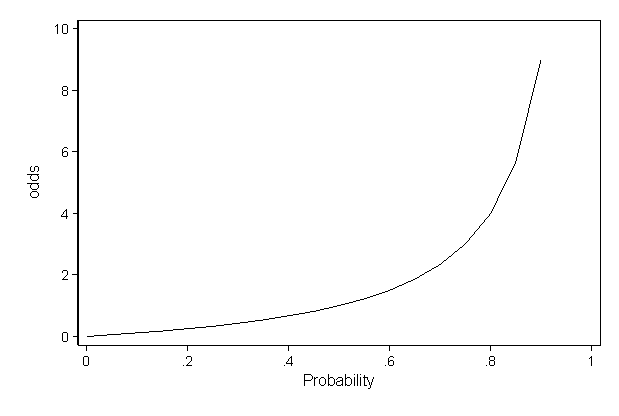
If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different concept The odds indicates how much more likely is an event to occur than not to occur (p/(1p))Figures etc Figure 1 Probability (P) vs Odds (O) where p=probability of success and q=probability ofRR = relative risk;



Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Proportion ( risk) ratio, but it is still the parameter of choice for many researchers Reasons for this include the fact that the odds ratio can be accurately estimated from casecontrol studies, while the risk ratio cannot Also, the odds ratio is the basis of logistic regression (used to study the influence of risk factors) Furthermore, theOdds = Probability / (1probability) Odds ratio (OR) = ratio of odds of event occurring in exposed vs unexposed group Odds ratio are used to estimate how strongly a variable is associated with the outcome of interest; On the other hand, if the risk in the unexposed group is 005, but the risk in the exposed group is 025, you still have a risk ratio of 5 But the risk difference is now 02!




12 Biostats Ideas Regression Analysis Linear Regression Chi Square



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk
OR = odds ratio; Comparing OR and Risk Ratio OR Farther from 1 The schematic below illustrates the point that, unless both the risk ratio and the odds ratio are 10 (no difference), The odds ratio is always farther from 10 than the risk ratio Larger if the risk ratio is greater than 10 and smaller if the risk ratio is less than 10Therefore, the importance of risk ratios depends upon the baseline risk




How To Calculate Odds Ratio In Microsoft Excel



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science
Odds Ratios vs Risk Ratios Posted on by StatsBySlough From the previous post, we understand that Odds Ratios (OR) and Risk Ratios (RR) can sometimes, but not always be interpreted in the same way We even saw that scientific studies made the mistake of interpreting odds ratios as risk ratios"Odds" is often known as the ratio of money that may be won versus the amount of money bet In statistics, an odds of an event is the ratio of − The probability that the event WILL occur to the probability that the event will NOT occur XFor example, in 100 births, the probability of a delivery being a boy is 51% and being a girl is 49%The magnitude of the odds ratio is called the "strength of the association" The further away an odds ratio is from 10, the more likely it is that the relationship between the exposure and the disease is causal For example, an odds ratio of 12 is above 10, but is not a strong association An odds ratio of 10 suggests a stronger association
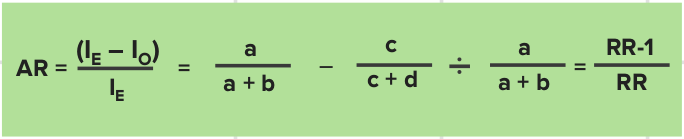



Attributable Risk And Odds Ratio Online Medical Library



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
R C = absolute risk in the unexposed group, given as a fraction (for example fill in 10% risk as 01) Confusion and exaggeration Odds ratios have often been confused with relative risk in medical literature Example (same example, but we will compute the odds ratio instead of the risk ratio) OR= (992/2260) / (165/1017) = 0439/0162 = 271 Step 1 Find the natural log of OR Step 2 Find the confidence limits on the natural log scale Step 3 Convert the log limits back to a linear scale by exponentiating themThe odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram
For estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithmThe prevalence ratio can also be calculated from the information on CHD and physical activity It is preferable to calculate the prevalence odds ratio when the period for being at risk of developing the outcome extends over a considerable time (months to years) as it does in this example PR = (a/N1) / (c/N0) PR= (50/250) / (50/750) = 30The odds ratio (OR) is a measure of how strongly an event is associated with exposure The odds ratio is a ratio of two sets of odds the odds of the event occurring in an exposed group versus the odds of the event occurring in a nonexposed group Odds ratios commonly are used to report casecontrol studies The odds ratio helps identify how likely an exposure is to lead to a specific




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notThe formula can also be presented as (a × d)/ (b × c) (this is called the crossproduct) The result is the same (17 × 248) = (/4216) = 371 The result of an odds ratio is interpreted as follows The patients who received standard care died 371 times more often than patients treated with theRelative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / Probability




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect
Odds ratio and relative riskAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators So if the probability of having liver disease among habitual alcoholic beverage drinkers is % and among nonalcoholic beverage drinkers is 2% the OR will be = %/ (1%) / 2%/ (21%/)=1225 and the RR of having liver disease when drinking alcoholic beverages will be = %/2%=10



Calculate Odds Ratio With 95 Confidence Intervals




Odds Ratio Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
When adjusted using logistic regression to control for other factors, the effects of the probiotic drink in reducing antibiotic associated diarrhoea remained (odds ratio 025, 95% CI 007 to 085) The researchers concluded that consumption of the probiotic drink reduced the incidence of antibiotic associated diarrhoeaRef=reference category Table A PORs are reciprocals of each other and pvalues are the same regardless of which outcome (yes or no) is modelled The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal



Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To
Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;For example, a risk of 05 is equivalent to an odds of 1; What's the Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios, Odds Ratios, and Hazard Ratios?




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Pdf Distributional Interaction Interpretational Problems When Using Incidence Odds Ratios To Assess Interaction




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy



Effect Sizes For 2 2 Contingency Tables



27 Sep 01 Draft




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Sas Different Odds Ratio From Proc Freq Proc Logistic Stack Overflow



Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download



Www Nature Com Articles Pcrj006 Pdf Origin Ppub




Relative And Atribute Risk




Random And Systematic Errors In Case Control Studies Calculating The Injury Risk Of Driving Under The Influence Of Psychoactive Substances Sciencedirect
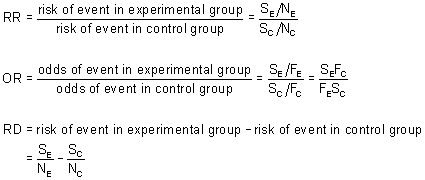



Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd




Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey
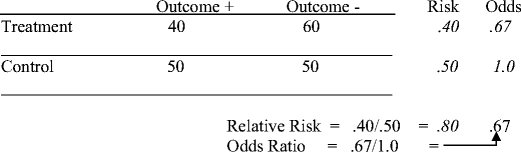



Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Springerlink
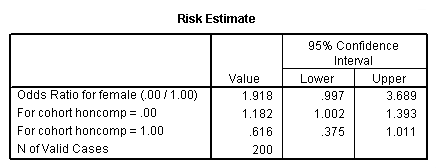



Logistic Regression Spss Annotated Output




Bravură Fii Entuziasmat Analitic Odds Ratio Calculator Callumluckwellfinalyear Com
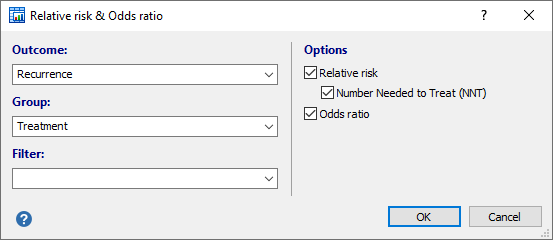



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




How To Calculate Odds Ratio In Microsoft Excel



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Calculating The Risk Ratio Odds Ratio And Risk Difference In A Randomised Controlled Trial Youtube




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss




Lecture3



Relative Risk Wikipedia




Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Ratio Chegg Com




R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow




Risk Differences And Rate Differences




Xmlinkhub




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough




In A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Estimates From Observational Studies Can I Pool Or With Hr And Rr Probably Not How Can I Transform Hr To Or




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy




File Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Svg Wikimedia Commons



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Table 1 From When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood



Table 2 From Interpretation Of Odds And Risk Ratios Semantic Scholar




Calculation And Interpretation Of Odds Ratio Or And Risk Ratio Rr Youtube



1




A Focused 08 Update On Methods For Cochrane




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science
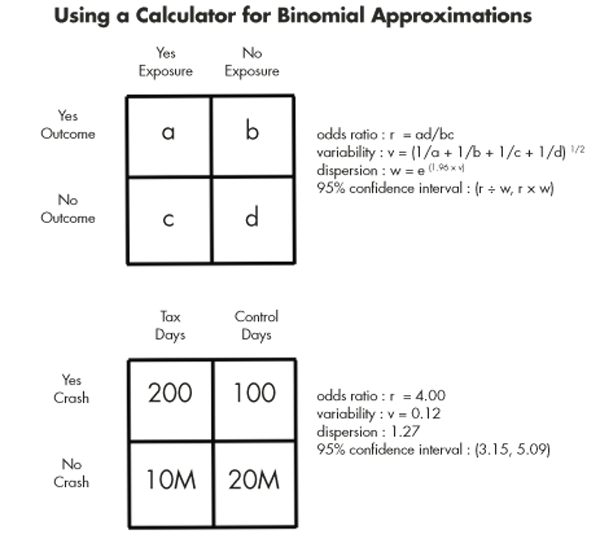



Online Odds Ratio Calculator 2x2 Odds Ratio In Rechnung Stellen Excel



Q Tbn And9gcs Pnxsjy3 X0gf842wm6tcfnesq2htc0kvu Tt2rst Svunqcb Usqp Cau
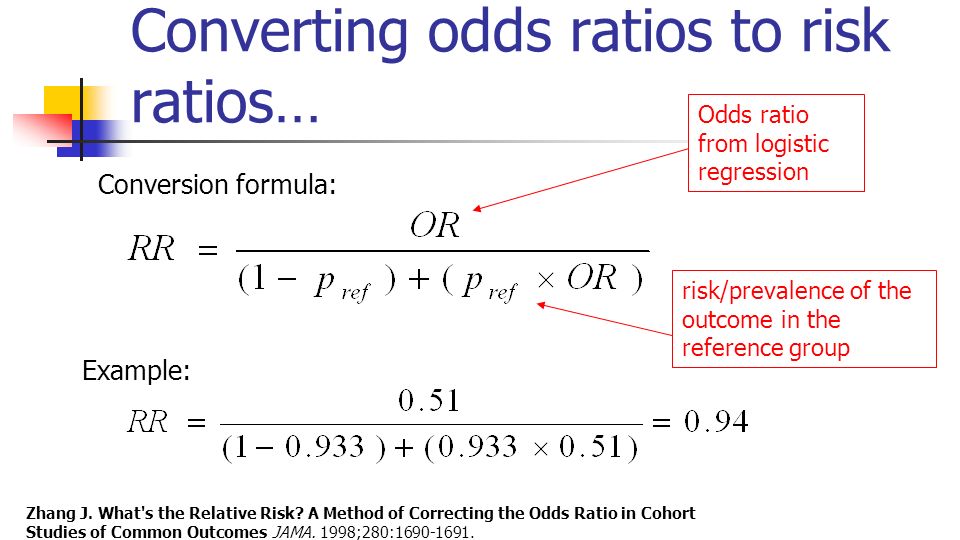



Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download
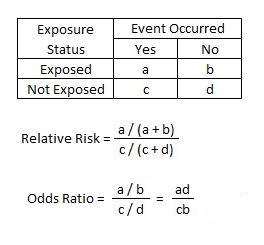



Relative Risk Article




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
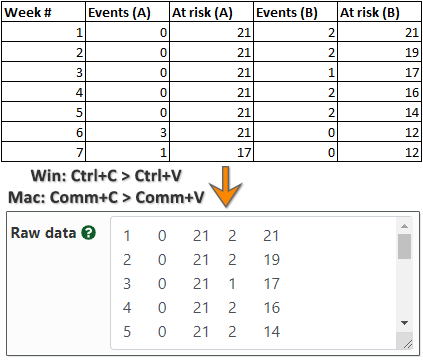



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value




Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Risk Ratio




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Meta Analysis Is A Summary Analysis Of More Studies Ecstep



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿